Battery provides convenience for us in this chaotic world. Various situations, applications, and users are pushing us to design and manufacture more advanced batteries and devices. So, in the manufacturing factory, how can we make the process manageable and analyzable for new designs? Let’s walk through the journey with our engineering analysts. Before getting the tickets for the journey, two questions may come to us. What are the battery manufacturing processes? How can the analytic methods help to manage these processes? First, let’s see the decomposed procedure in a manufacturing factory. As in figure 1, we can have five workshops to take charge of the different segmental production.
- Workshops I and II are responsible for the cathode and anode preparation from raw material mixing and electrode coating.
- After some necessary electrode processing (like tap welding, size/shape forming, density increasing by rolling, etc.), workshop III assembles two electrodes together with the polymer separator positioned between them. Either place the assembly in an iron cylinder or aluminum pouch. Then seal it from the air environment as soon as the liquid electrolyte is injected into the cell. The standard battery prototype is achieved.
- To create a suitable electrochemical environment inside the cell, the battery needs to go through the formation and aging in workshop IV. Charging the battery with increasing current density to activate the materials and making them ready for regular charge-discharge use while resting the battery at a specific temperature for a period. Testing the aged battery and distributing them into bins with different capacity ranges.
- The rest for a factory is to pack a set of batteries parallelly or serially into a module, which is called a packing process in workshop V. The battery management system will be integrated into the module to monitor the voltage, current, and the cycle life.
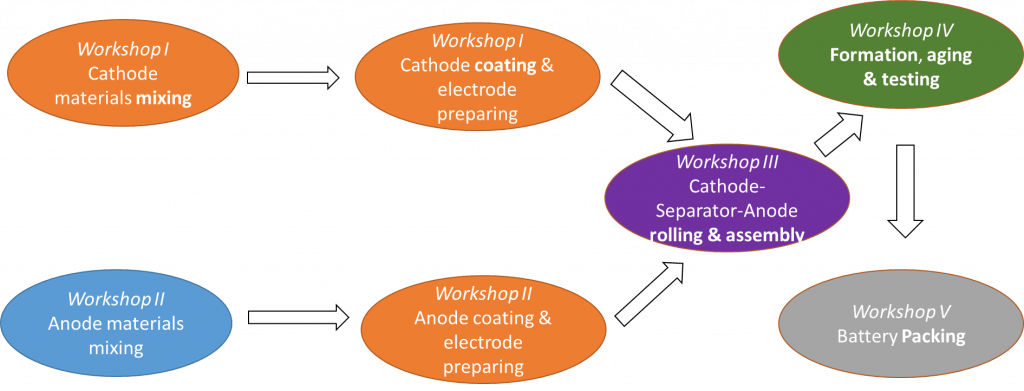
Fig. 1. The workshop divisions for the battery manufacturing
When incorporating the procedure diagrams with the workshop sequences, we can a battery manufacturing schematic as in Figure 2. Since multiple steps are involved in the manufacturing process and each step is influenced by a bunch of dependent or independent variables, the quality control throughout this factory is very much complicated. It needs advanced tools and great endeavors to optimize and further regularize the battery manufacturing process. As a potential direction, the data-powered system is wildly used in the industrial world. A discussion of this system will be seen in the next post.
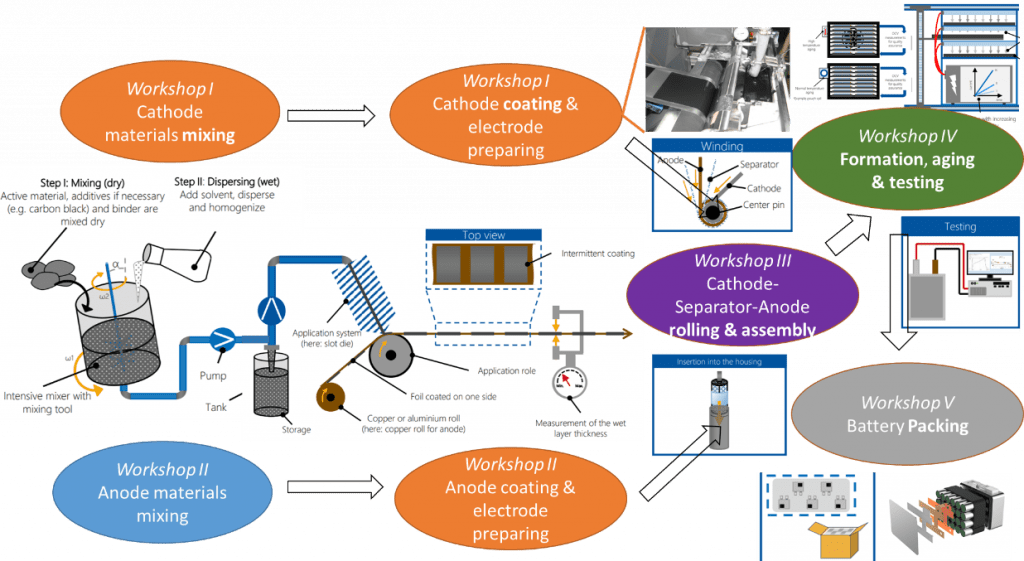
Fig. 2. The schematic of battery manufacturing with procedure diagrams.
(For more about manufacturing details, please read PEM der RWTH Aachen, VDMA, Lithium-ion battery cell production process, Battery Production, 3rd Edition, Frankfurt am Main, 2018)